All Resources
Grading open-ended responses is a complex and essential process in education, recruitment, and training. With AI-powered answer evaluation, organizations can significantly reduce manual workload while ensuring more objective, standardized, and consistent scoring.
According to a study from the University of Surrey, an AI-powered grading tool has the potential to revolutionize assessment, offering up to 80% time savings and full consistency in grading.
AI grading is the use of artificial intelligence to automatically evaluate and score open-ended questions such as short text answers, essays, audio and video responses, or coding tasks. Instead of a human grader, AI systems apply machine learning models and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze a candidate’s answers and provide results.
AI grading is the process of using artificial intelligence to automatically evaluate candidate responses based on predefined criteria. In practice, you provide the AI with the question, the candidate’s answer, and the evaluation criteria. The AI then analyzes the response against those criteria and generates a grade.
The clarity and detail of your instructions determine how AI grades. By giving the AI clear, detailed instructions or a rubric, you ensure more accurate and consistent grading that aligns with your expectations.
Different large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT (OpenAI), Gemini (Google DeepMind), and Claude (Anthropic) can all be used for AI evaluation. Each of these providers offers multiple model versions that vary in capabilities.
TestInvite provides the flexibility to integrate with different AI models depending on your assessment needs. Instead of relying on a single provider, TestInvite allows you to choose the AI model best suited for each question type.
AI-assisted grading system saves evaluators significant time and effort compared to manual grading.
While creating the question, the author provides the AI model with instructions and scoring guidelines that define how the response should be evaluated. For short-answer questions, the AI combines the candidate’s response with the question and the instructions, and evaluates aspects such as accuracy, relevance, and completeness. Using the provided instructions and scoring guidelines, it then automatically generates a grade.

Context:
The test taker is a high school student taking a history exam. The answer is expected to demonstrate basic historical knowledge, clear explanation, and simple but correct language.
Evaluation criteria:
A correct response must mention at least one valid reason, such as:
Accept paraphrased answers that clearly convey the meaning of one of these reasons.
For essay questions, the AI takes the candidate’s written response together with the original question and the accompanying instructions. It then evaluates the essay across multiple dimensions, such as grammar, vocabulary range and precision, logical flow and coherence between paragraphs, overall structure, and the accuracy with which the candidate addresses the question. By aligning this analysis with the provided instructions and scoring guidelines, the system automatically generates a grade that reflects both the content and the quality of writing.
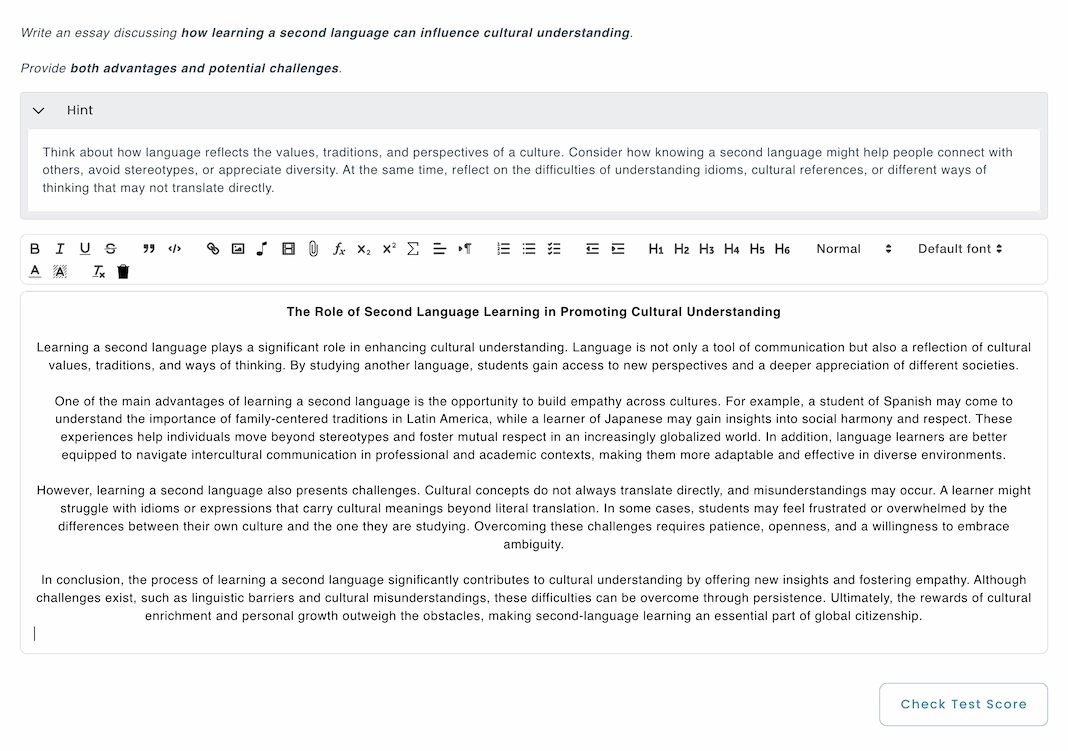
Context:
The test taker is a college student majoring in Languages. The essay should demonstrate academic writing skills, rich vocabulary, and clear argumentation.
Evaluation criteria:
1. Content & Relevance (40%)
2. Structure & Organization (20%)
3. Language & Vocabulary (40%)
For speaking questions, the candidate’s audio response is first converted into text using speech recognition. Once converted to text, the AI conducts a detailed analysis, assessing dimensions such as accuracy, fluency, lexical choice, and relevance in relation to the defined scoring guidelines. Based on this analysis, the system automatically generates a grade that reflects both content quality and language performance.
Context:
The test taker is a job applicant taking a pre-employment speaking assessment. The response will be evaluated based on clarity, organization, and language use in a workplace context.
Evaluation criteria:
1.Content & Relevance (40%)
2.Organization & Coherence (20%)
Clear beginning, middle, and conclusion.
Logical flow of ideas with smooth transitions.
3.Language & Fluency (40%)
For video questions, the candidate’s recorded response is first transcribed into text using speech recognition. The AI then evaluates both the transcript and the audio-visual features of the response, such as pronunciation, fluency, clarity, and delivery. These elements are aligned with the given instructions and scoring guidelines, enabling the system to automatically generate a grade that reflects both verbal accuracy and communication skills.
Context:
The test taker is a working professional in a corporate environment. The question is designed to assess the content structure, communication skills, and grammar.
Evaluation criteria:
1. Content & Structure (40%)
The response should follow the STAR framework:
Score high if all elements are covered with clarity and relevance.
2. Communication & Soft Skills (30%)
3. Grammar & Fluency (30%)
For coding questions, the candidate’s submission is compiled and executed against a set of predefined test cases. The AI evaluates not only whether the code produces correct outputs but also its efficiency, readability, and adherence to the given requirements. This evaluation is aligned with the provided scoring guidelines, enabling the system to automatically generate a grade that reflects both functional accuracy and coding quality.
Context
The test taker is a junior backend developer candidate. Evaluate the submitted Python 3 code and its behavior (no external packages). Focus on correctness first; simple, readable solutions are acceptable.
Evaluation Criteria
1.Correctness (60%)
2.Code Quality & Readability (25%)
3.Efficiency (15%)
A study published in the British Educational Research Journal in 2024 found that AI grading is generally accurate, with results that often resemble human scoring and can even be mistaken for it at first glance. While statistical differences between AI and human graders can be found, this assumes that the human grader is always the benchmark. In reality, even human graders can differ significantly from each other, so AI’s performance is considered reasonably consistent and reliable. [2]
As discussed in the publication The Role of AI in Automating Grading: Enhancing Feedback and Efficiency (2024), AI grading can be ethical if it is implemented with safeguards to ensure fairness, accountability, and inclusivity. [3]
The ethical challenges of AI grading center on fairness, transparency, and accountability. AI systems must operate impartially across demographic groups, with regular checks for bias. Users should be informed about how the system works, have a choice in its use, and access to human oversight and appeal processes. Ultimately, AI should be designed to support human decision-making rather than replace it, ensuring trust, fairness, and inclusivity in its applications.
AI-assisted grading often requires collecting and processing sensitive personal information, such as written essays, recorded speech, video responses, or even biometric data. Protecting this data requires strong encryption and cybersecurity measures, anonymization to remove identifiable information, compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR, and transparency about what data are collected and how they are used. Consent is also essential, and organizations must ensure that technology providers follow strict privacy standards.
As artificial intelligence continues to develop, grading systems may begin to handle more sophisticated and diverse assignments. Advances in natural language processing and machine learning could enable the evaluation of not only technical accuracy but also creativity, argument quality, and presentation in essays, research work, and multimedia projects. This way, AI can provide more nuanced assessments.